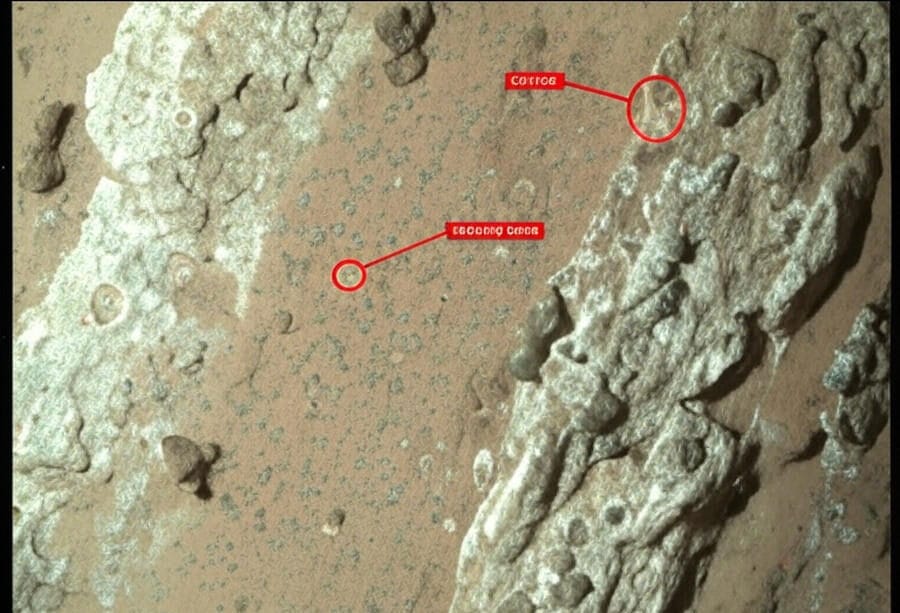
On September 12, 2025, NASA announced a monumental discovery: the Perseverance rover detected organic compounds in Martian rocks, offering the most compelling evidence yet of potential ancient microbial life on Mars. This Mars life discovery, found in the Jezero Crater, has captivated scientists and the public alike, sparking renewed excitement about the Red Planet’s past habitability. While not definitive proof of life, these organic molecules are a critical clue, suggesting Mars may have once hosted conditions suitable for microbial organisms. As NASA prepares for the ambitious Mars Sample Return mission to analyze these samples on Earth, this breakthrough underscores the importance of continued exploration. This article explores the discovery’s details, scientific significance, and future implications, optimized for readers seeking insights into the Mars life discovery.
What Perseverance Found
Organic Compounds in Jezero Crater
Since landing in February 2021, NASA’s Perseverance rover has been exploring Jezero Crater, a 28-mile-wide basin believed to have been a lake billions of years ago. Using its SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument, the rover identified carbon-rich organic molecules in rock samples. These compounds, often associated with biological processes on Earth, are the strongest hint yet of a possible Martian biosphere. The Mars life discovery, while not confirming life, suggests that Jezero’s ancient environment could have supported microbial activity.
Why This Finding Stands Out
The presence of organic compounds is significant because they are the building blocks of life, containing carbon, hydrogen, and other elements essential for biological processes. Unlike previous missions, which detected simpler organics, Perseverance’s samples show complex molecular structures, indicating a potentially richer chemical environment. Dr. Sarah Martinez, a planetary scientist at NASA, stated, “This Mars life discovery is a game-changer. It’s not just about finding organics—it’s about their complexity and context in a once-wet environment.” The discovery aligns with Jezero’s geological history, where water and sediment deposits created conditions favorable for life.
Scientific Context and Implications
Mars’ Ancient Habitability
Billions of years ago, Mars boasted liquid water, volcanic activity, and a thicker atmosphere, resembling Earth’s early conditions. The Mars life discovery strengthens the hypothesis that Mars was once habitable, with Jezero Crater serving as a prime target due to its ancient river delta. The organic compounds could result from biological processes, such as microbial metabolism, or abiotic processes, like chemical reactions driven by volcanic heat or meteorite impacts. Distinguishing between these origins is the next challenge, but the findings narrow the gap in understanding Mars’ potential to host life.
Building on Past Missions
The Mars life discovery builds on decades of exploration. The Viking landers in the 1970s provided early hints of organic material, while the Curiosity rover’s 2018 detection of methane and simple organics in Gale Crater set the stage for Perseverance’s work. Unlike its predecessors, Perseverance’s advanced instruments allow for precise chemical analysis, revealing more complex organic signatures. This progression highlights technological advancements and reinforces the strategic selection of Jezero Crater as a scientific goldmine.
Implications for Astrobiology
The Mars life discovery has far-reaching implications for astrobiology, the study of life in the universe. It informs future missions to other potentially habitable worlds, such as Jupiter’s moon Europa or Saturn’s moon Titan. The techniques used by Perseverance, like Raman spectroscopy, could be adapted for these missions, enhancing our ability to detect biosignatures in diverse environments. The discovery also fuels debates about the definition of life and how to identify it beyond Earth, pushing scientists to refine their criteria.
Mars Sample Return
Planning the Sample Return Mission

To confirm whether these organic compounds indicate past life, NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) are developing the Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission. Perseverance has cached over 20 rock and soil samples in sealed titanium tubes, which a future spacecraft will retrieve and return to Earth. Scheduled for the late 2020s, the MSR mission will allow scientists to analyze the samples using advanced laboratory instruments, capable of detecting isotopic ratios and molecular patterns that rovers cannot.
Technical and Financial Challenges
The MSR mission is one of NASA’s most ambitious endeavors, with estimated costs of $8-11 billion. Challenges include designing a spacecraft to launch from Mars’ surface and ensuring sample integrity during the journey. Despite these hurdles, experts are optimistic. Dr. Rajesh Patel, a geochemist, noted, “Earth-based analysis could reveal biosignatures that confirm the Mars life discovery, rewriting our understanding of the cosmos.” The mission’s success hinges on international collaboration and sustained funding.
Global Impact and Public Engagement
Inspiring a New Generation
The Mars life discovery has ignited global fascination, dominating headlines and social media. Educational institutions are using the news to promote STEM programs, while NASA’s outreach efforts, including virtual tours of Jezero Crater, engage young audiences. The discovery underscores the value of space exploration in inspiring curiosity and innovation, with potential to shape future careers in science and technology.
Cultural and Philosophical Significance
Beyond science, the Mars life discovery prompts profound questions about humanity’s place in the universe. If confirmed, evidence of Martian life could challenge philosophical and cultural perspectives, sparking discussions about life’s origins and prevalence. Public interest in the discovery also strengthens advocacy for increased space exploration funding, as governments and private entities recognize its scientific and societal impact.
Conclusion
NASA’s Perseverance rover has delivered a historic Mars life discovery, detecting organic compounds that hint at ancient microbial life in Jezero Crater. While not conclusive, this finding marks a significant step in the search for extraterrestrial life, building on decades of exploration and setting the stage for the Mars Sample Return mission. As scientists await the opportunity to analyze these samples on Earth, the discovery fuels global curiosity and underscores the importance of continued investment in space research. The Red Planet continues to captivate, holding secrets that may soon redefine our understanding of life in the universe.







